This advanced malware uses tactics and techniques to evade detection by traditional anti-malware tools. These techniques include technical evasion methods and the exploitation of human beings using social engineering and phishing. Older anti-malware technology that uses malware 'signatures' to detect cyber-attacks is no longer effective as modern malware does not use or hide these signatures.
Modern malware can, for example, be fileless, polymorphic, and metamorphic. These terms reflect the adaptive nature of modern malware. Polymorphic malware, for example, can adapt to conditions; the malware uses self-propagating code to adjust to environmental factors, such as already installed traditional anti-malware, to evade detection.
Advanced malware tactics may also involve utilizing older malware strains but changing elements such as delivery methods. These malware modifications have led to advances in developing security solutions that are intelligent enough to spot how evasive malware strains operate.
Modern malware can, for example, be fileless, polymorphic, and metamorphic. These terms reflect the adaptive nature of modern malware. Polymorphic malware, for example, can adapt to conditions; the malware uses self-propagating code to adjust to environmental factors, such as already installed traditional anti-malware, to evade detection.
Advanced malware tactics may also involve utilizing older malware strains but changing elements such as delivery methods. These malware modifications have led to advances in developing security solutions that are intelligent enough to spot how evasive malware strains operate.
Did You Know?
cyber attacks begin with phishing
to seamlessly install PhishTitan
estimated global cybercrime cost
to stop & spot a phishing attack
Examples of Advanced Malware
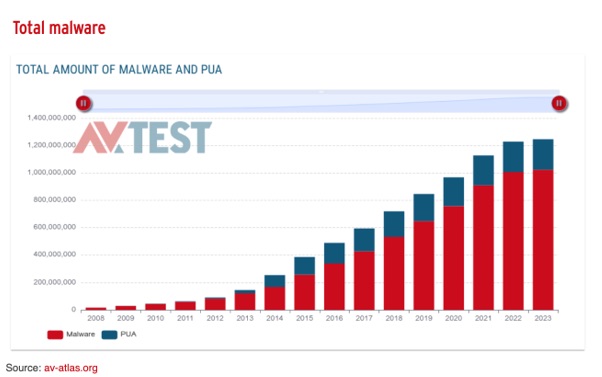
The AV-Test Institute registers over 450,000 new malware and potentially unwanted applications (PUA) strains daily; the numbers of new malware only seem to increase, as the graph below demonstrates.
Advanced malware is often used to target specific industries, such as the finance or healthcare sectors. Advanced malware also often targets particular individuals or roles in an organization, such as the CEO, IT administrator, or accounts payable employees. The targeting of employees is typically based on phishing emails and often involves social engineering.
Some examples of recent advanced malware attacks show the type of tactics used to evade detection:
Advanced malware is often used to target specific industries, such as the finance or healthcare sectors. Advanced malware also often targets particular individuals or roles in an organization, such as the CEO, IT administrator, or accounts payable employees. The targeting of employees is typically based on phishing emails and often involves social engineering.
Some examples of recent advanced malware attacks show the type of tactics used to evade detection:
Fileless Attack
'Fileless malware' is a term used to describe malware that does not rely on files or uses files only in specific parts of the attack chain to carry out an infection. The EternalBlue cyber threat was based on a fileless attack. EternalBlue was behind the UIWIX and Petya ransomware attacks.
Fileless malware attacks are challenging to detect, as the malware exploits legitimate software tools installed on computers. For example, some types of fileless malware can write malicious code directly to the Windows registry using a specialized program known as a 'dropper.' The code resides in native files, and traditional anti-malware software cannot detect the invasion. In addition, fileless ransomware may use ubiquitous tools such as Microsoft PowerShell to encrypt files without writing anything to disk.
Polymorphic Malware
Evading detection by dynamically adapting to conditions is a core evolutionary strategy polymorphic malware uses. The credential-stealing Emotet malware is an example of a highly successful polymorphic malware strain. Emotet is a banking trojan that uses phishing emails to spread malware. Polymorphic malware is highly adaptive and can recognize the conditions of an infected machine; for example, Emotet can detect if the code is in a virtual machine environment and lie dormant. In addition, polymorphic malware uses an encryption key to change code, using encryption to scramble the code so it appears different.
Metamorphic Malware
Metamorphic is a highly advanced malware, a step-up from polymorphic malware with the ability to rewrite its code. Metamorphic malware is exceptionally adaptive and may use machine learning to help the malware morph. The malware code is continuously rewritten, with each version different from the last. This ever-changing code makes detection challenging. Tardigrade malware, used to target the manufacturing sector, is an example of metamorphic malware.
AI-driven malware detection uses real-world data across a massive threat corpus to keep one step ahead of advanced malware.
Advanced Malware Protection
Advanced malware evasion requires advanced malware protection. Traditional antivirus solutions can no longer rely on detection methods such as signature engines; traditional antivirus solutions can only be used to detect known malware based on signatures or heuristics (code sequences). This Achilles Heel of conventional malware detection methods is exploited by polymorphic, fileless, and now metamorphic malware. Advanced malware protection solutions do not rely on known signatures. Instead, advanced malware detection is based on spotting specific behaviors used by modern malware and using tactics such as sandboxing and deep examination of potential threats. This allows the detection of previously unknown strains, as the malware protection solution is designed to look for advanced malware tactics such as downloading executables from the internet.
Advanced malware protection should apply layers of protection to ensure that all types of traditional and advanced malware are caught. The essential layers should include the following:
The First Line Of Defense Detection
Even advanced malware detection methods should detect conventional malware that can be identified using signature-based detection.
AI-Driven Threat Detection
Malware detection engines should be driven using AI trained to spot nascent malware threats. AI-driven malware detection uses real-world data across a massive threat corpus to keep one step ahead of advanced malware.
Behavior-Driven Malware Detection
A vital layer in advanced malware detection is behavioral analysis to check for any suspicious behavior on a system. This suspicious behaviour can include unusual file downloads and file extraction or compression. The behavioral analysis can also include activities such as lateral movements. In addition, the behavioral analysis will work with AI-driven engines to look for new and emerging threats.
Sandboxing
Another essential layer in malware detection and prevention is the ability of a malware protection solution to create sandboxes. Sandboxing refers to a controlled, virtual environment that isolates and monitors the danger of a specific incoming file. For example, Sandboxing is a great way to monitor an incoming email attachment; the sandbox runs the file in a controlled environment to see if the file is malicious. The file is then either quarantined for destruction or released to the recipient.
Using AI-Driven Malware Protection To Detect And Prevent Advanced Malware
Advanced malware protection uses AI-enabled phishing protection to stop malware that morphs. These intelligent anti-malware solutions can also prevent advanced attacks that rely on exploits of (as yet) unknown vulnerabilities such as 'zero minute' attacks. PhishTitan is an example of an intelligent malware detection solution that uses a comprehensive, AI-enabled mechanism to detect advanced malware attacks. PhishTitan uses modern threat intelligence to contain threats quickly. This level of deep threat detection using AI is essential to tackle the advanced capabilities of modern malware.
Because cyber criminals often begin their attack chain by targeting employees, advanced malware detection solutions will begin the threat hunt as emails enter the system. This starting point is essential because polymorphic malware will use adaptive attack methods to modify malicious URLs that link to websites in a phishing email to evade detection by traditional email gateways.
An AI-driven malware detection solution, such as PhishTitan, prevents polymorphic malware from exploiting this technique by examining the link in an inspection site to check the website's validity associated with the link. If the website is phishing, the user will be stopped from entering the website.
AI-driven threat detection and prevention applies a layered series of protection methods, including:
AI-Driven Threat Intelligence: AI training relies on vast amounts of real-world data. These data reflect the type of threats in the landscape. For example, advanced malware detection uses AI-driven threat intelligence to keep up to date with the latest malware threats. The AI engine will generate alerts if any dangerous URLs and web pages are detected; this detection is also used to prevent employees from clicking links or navigating to malicious websites.
Multi-Layered Email Gateway Protection: a multiplex of sophisticated detection methods is used to detect malware, including traditional malware, advanced strains, and spam.
Time Of Click Protection: as described earlier, 'time of click' protection will stop malicious URLs from tricking employees into enterprising login credentials and other information into phishing websites. This real-time protection is vital in addressing modern advanced malware threats' polymorphic and metamorphic nature.
Real-Time Threat Analysis: real-time analysis of threats is essential in tackling modern malware. As malware code adjusts to conditions and new strains enter the threat landscape, a fast, real-time response to malware threats is the only way to respond.
Link Lock Service: AI-driven detection requires appropriate responses that do not interfere with legitimate emails and maintain work productivity. Advanced malware detection solutions should offer services such as a Link Lock to ensure they are still protected even if an employee clicks a URL in a malicious email.
PhishTitan For Advanced Malware Detection
We developed PhishTitan to tackle the most advanced of modern malware threats. The AI-driven engine behind PhishTitan provides all the protection needed to stop advanced malware before it damages a network, steals credentials, or installs ransomware. Advanced malware detection is challenging, but by fighting these insidious threats with an intelligent solution such as PhishTitan, an organization knows it is applying the best solution to adaptive and deceptive cyber-attacks.
How to Avoid Credential Harvesting and Email Spoofing Attacks
The complex and often multi-part cyber-attacks that revolve around the theft of credentials require a layered approach to security. The following measures are essential to protect your business against these attacks:
Train Employees
A baseline response to email spoofing and credential harvesting is to use employee security awareness training. Awareness training should include interactive exercises that teach employees to spot tell-tale signs of spoofed emails. Add to this training simulated phishing exercises. A simulated phishing platform, like SafeTitan, delivers fake phishing emails to employees to train them to recognize attempts to steal credentials.
Use Multiple-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) uses multiple layers of credentials to log in to an app or other network resource. MFA is an important layer of security. Deploying MFA adds a layer of difficulty in hacking into networks or email accounts. However, MFA alone is not enough to deter determined hackers.
Report Spoofing and Phishing
Any suspected incidents of spoofing or phishing must be reported. This allows your security team to triage the incident. Teach your employees about the importance of incident reporting and ensure that they are encouraged, not discouraged, from reporting.
Set Up Anti-Spoofing Processes.
Set in place checks and measures to help prevent the outcomes of spoofing and credential harvesting. For example, double-check payments over a certain amount.
Deploy Advanced Anti-Phishing Tools
Cybercriminals intent on spoofing emails and harvesting credentials will stop at nothing. They use various techniques as part of a chain of attack. Breaking this chain is essential to preventing a cyberattack like Business Email Compromise. PhishTitan uses machine learning detection models to detect malicious content, like an email link to a spoof website. PhishTitan also applies Natural Language Processing (NLP) to spot social engineering and other complex trust-based cyberattacks.

Susan Morrow
- DATA PROTECTION
- EMAIL PHISING
- EMAIL SECURITY
Talk to our Team today


